Family Tree Visualization for Blended Families
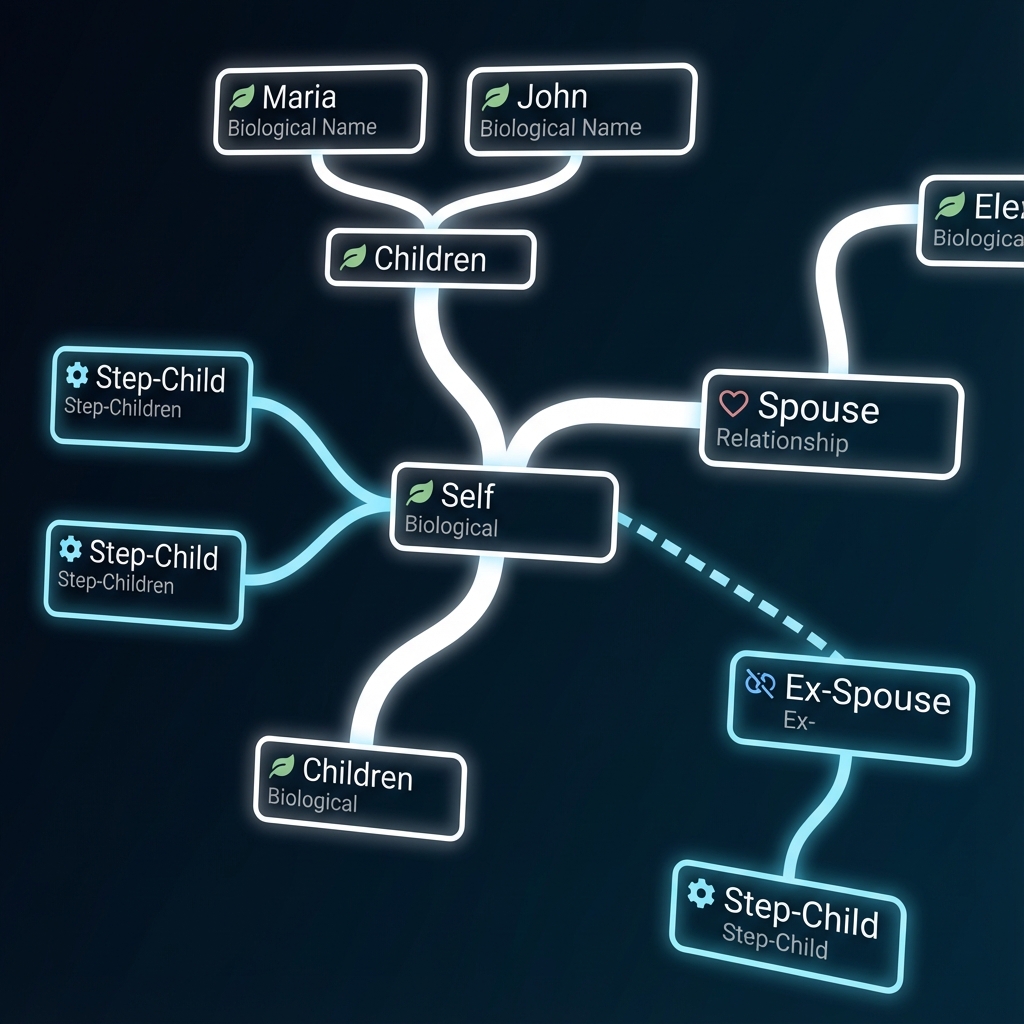
The nuclear family of the 1950s—mom, dad, and biological kids—is no longer the default. Blended families, second marriages, and step-children create a web of relationships that standard "I love you" wills cannot address. In these high-stakes scenarios, a simple text description of "descendants" creates ambiguity where clarity is catastrophic.
This article outlines why family tree visualization is mandatory for modern blended family planning.
Key Concepts
Managing blended family dynamics requires rigorous definition of relationships and flow.
- Relationship Ambiguity — The legal confusion between "children," "step-children," and "adopted children."
- Disinheritance Risk — The unintentional exclusion of family members due to broad drafting.
- Stakeholder Maps — A visual confirmation of who is in the family and, crucially, who is out.
Relationship Ambiguity
Does a bequest to "my grandchildren" include the step-grandchildren from a second marriage? In many states, the default answer is no. If a client assumes yes, a family war begins.
Visual family trees force these questions to the surface during the design phase. By literally drawing the lines of descent, attorneys and clients identify the gaps in their definitions.
Disinheritance Risk
The most common tragedy in blended families occurs when spouses leave everything to each other, assuming the survivor will "take care of" the step-kids. Often, they don't.
Visualizing the flow of funds shows the "lock-out" scenario clearly: simple wills mean the first spouse's children can be completely disinherited by the second spouse's whim.
Conclusion
In blended families, assumption is the mother of all lawsuits. You cannot rely on standard definitions or implied understandings.
A visual family tree acts as the architectural blueprint for the estate plan, ensuring that the legal structure matches the biological and emotional reality of the family.
Frequently Asked Questions
Should we show the diagram to the beneficiaries?
It is often helpful to walk the adult children through the flow to manage expectations and explain protections.
How deep should the tree go?
Usually three generations (Parties, Children, Grandchildren) is sufficient to spot 90% of planning issues.
How do we handle estranged children?
Mark them clearly on the internal diagram, but exercise caution in what is shown to the family to avoid conflict.
Sources & Further Reading
Read More Articles
How four specialized components turn complex legal rules into deterministic, client-ready documents using the Velcro Model of Law.
Read Article
Ontology as Infrastructure
Why a legal ontology is not a taxonomy, and why it must behave more like infrastructure than metadata.
Read Article
Mapping the Legal Universe
How we extract, filter, and map rules of law across statutes to build a navigable legal universe.
Read Article